General Metadata Properties
In addition to properties which affect the individual functionality of each metadata, there are also general properties common to all metadata.
Common metadata properties are provided by the metadata entity type, which is the super type for all other metadata types. There are several properties that are common to each metadata type, and each provide a specific function regarding the behavior of the subtype instance.
ID
An automatically generated ID, configured when you first commit an instance of a metadata. The ID is of the type Object : Long.
Conflict Priority
The Conflict Priority property is used to decide between conflicting metadata. Conflict Priority is of the type double.
This metadata property is essentially a decimal number between 0 and 1. It is used to decide which metadata to use if there is more than one instance of the same metadata. The higher the number the more likely it is to be used.
If there are two metadata that are both of the same type, the conflict priority is used to determine which metadata is used. It is also used to decide between a metadata defined locally (that is, define directly on the type to which it belongs) or metadata inherited from a super type. However, in this circumstance the locally defined property is always used unless the important Boolean has been set to true in the super type where the metadata was inherited from.
Example
If you have a model, entity or property that has more than one metadata that is either the same, or causes a conflict, you can assign a decimal value to each metadata. Each metadata value should be between 0 and 1, expressed as a decimal number.
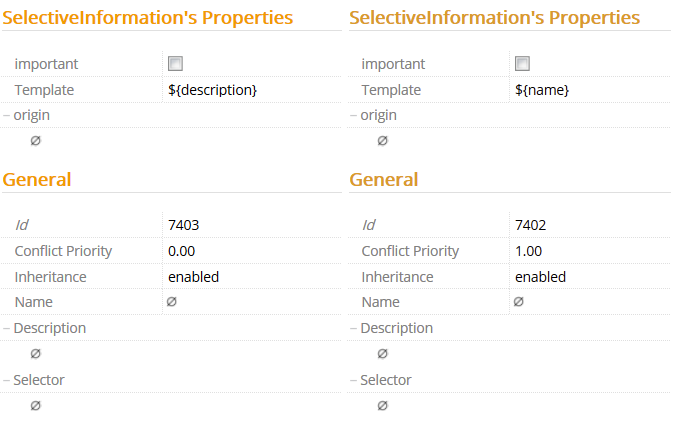
The two SelectiveInformation metadata are in conflict when displayed in Explorer. However, the metadata with the conflict priority of the value 1.0 (the one with the template ${name}) is going to be displayed thanks to the higher value of the Conflict Priority property.
Important
You can use the Important property to boost the priority of inherited metadata. Important is of the type Boolean.
In the case where you have the same metadata defined in the supertype and in its subtype, the inherited metadata has lower priority. If the Important property is set on an inherited metadata, the metadata is resolved as if it was defined locally on that entity and not inherited from the entity's supertype. When this property is set to false, any metadata defined locally, that is, the metadata defined on the entity or property, is automatically selected. If you decide to use inherited metadata, you can have tribefire treat that metadata as if it was defined locally by enabling the Important property. Then, the normal conflict priority decision is made when the system resolves the metadata. A conflict priority property then decides between the two values of the metadata and selects the one with the higher value.
Example
In this example, we consider an entity called Address which has a supertype called StandardIdentifiable. Both have the metadata Entity Type Display Info. The supertype's metadata has the important field set to false. This means that the value of the metadata in the subtype (Address) is used, even though the value of the supertype's Conflict Priority is higher. If you set the important property in the metadata of the supertype to true, the Conflict Priority values are used to decide which metadata should be used.
Inherited
This metadata property allows you to define whether the metadata is inherited in subtypes, depending on which element this metadata is assigned to. There are two possible values: enabled (checkbox selected) or disabled (checkbox cleared). The default value is enabled.
If the value of this property is set to enabled, the metadata's functionality is inherited in the subtype entities, properties, or enums. However, if the value of this property is set to disabled, then the metadata is not inherited and has no effect on the subtype's inherited elements.
Example
In this example we consider an entity type called Organization, which has various properties, including headquartersLocation. A subtype of Organization is called Company, which inherits this property. headquartersLocation has a Property Display Info metadata with the value headquartersLocation attached to it.
-
If you set the value of inherited to enabled, the metadata's functionality is inherited along with the entity, property or enum to which it belongs.

-
If you set the value of inherited to disabled, the metadata's functionality is not inherited.
